Local Storage seems to be disabled in your browser.
For the best experience on our site, be sure to turn on Local Storage in your browser.
Mechanical Engineering


COMPRESSED AIR TECHNOLOGY IN MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
Pneumatics finds its application in mechanical engineering for various reasons, primarily for process automation and generating mechanical motion using compressed air.
COMPRESSED AIR TECHNOLOGY IN MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
Below are some of the key applications of pneumatics in mechanical engineering:
- Motion control
- Automation
- Energy efficiency
- Safety
- Explosive environments
- Lightweight construction
- Control and regulation
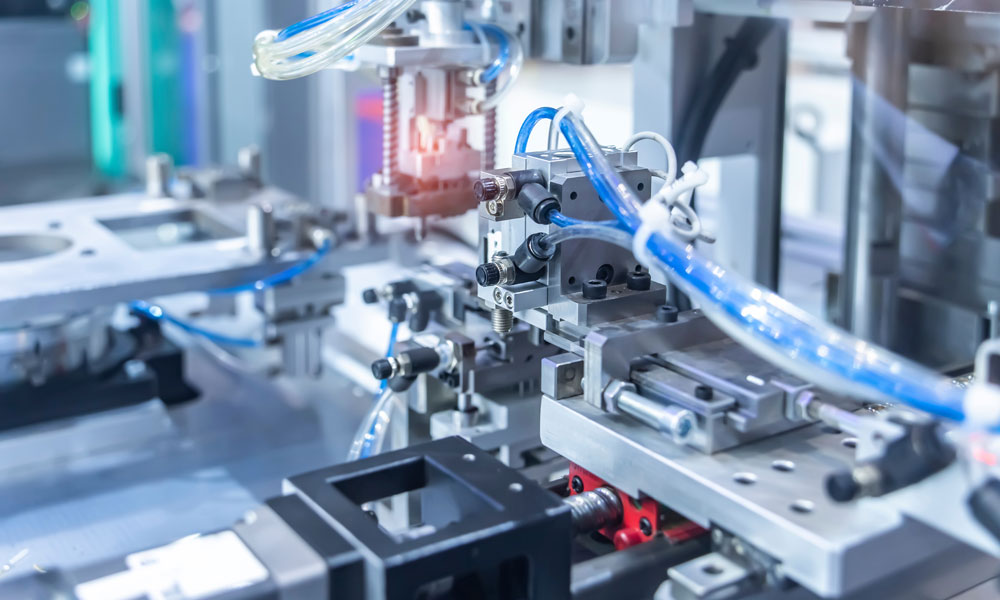


PNEUMATIC DRIVES
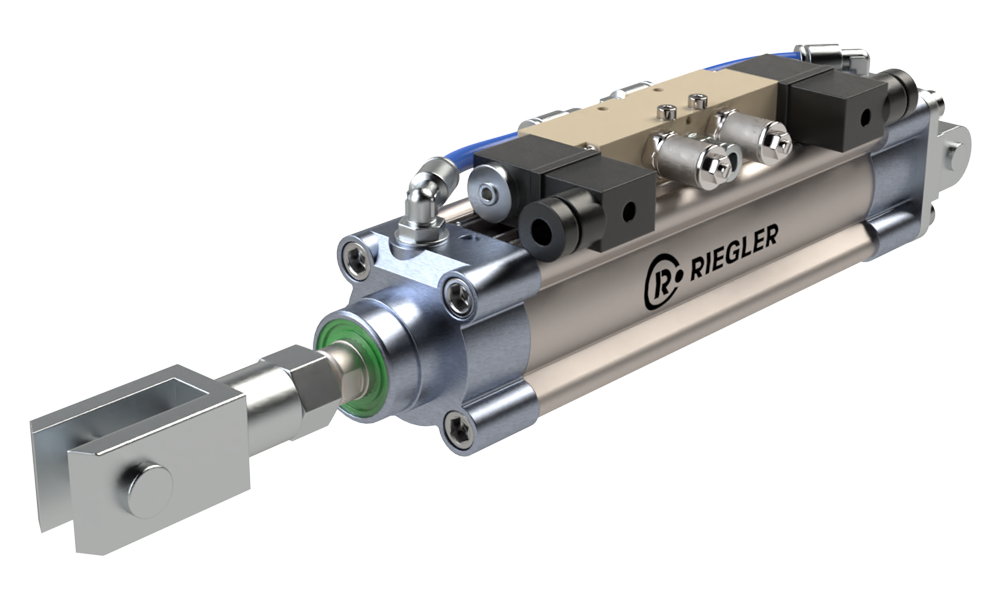

Ready-to-install pneumatic drives for processing technology.
- Ready-to-install
- ATEX approval
Individual cylinder units including solenoid valves, attachments, and sensors for use in ATEX environments. The units control dosing valves within the explosion hazardous space of a mixing plant.
CLAMPING CYLINDERS / CONSTRUCTION COMPONENTS
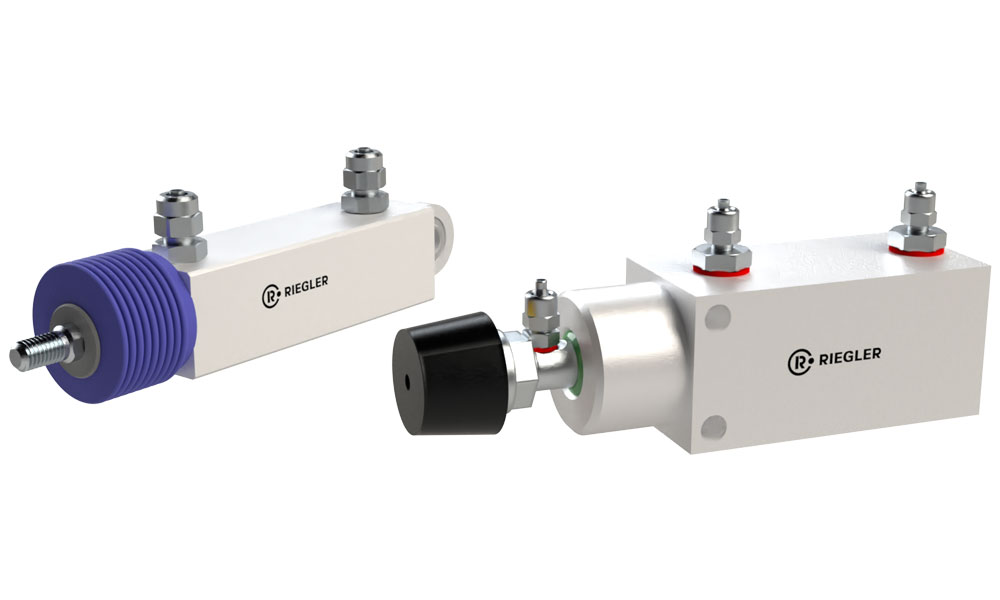


Construction cylinders for packaging machines that are specially adapted to the installation space.
- Also available in a food-safe version
Clamping cylinders that are specially designed for the processing of packaging material in a packaging machine.
ATEX ACTUATION UNITS FOR SLIDE VALVES
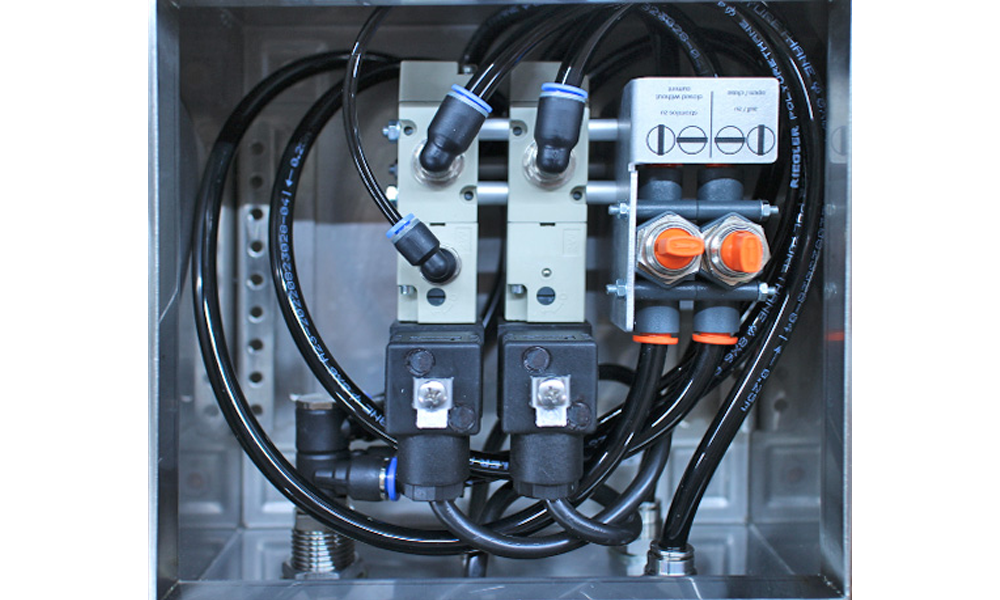

Actuation units for slide valves for the pharmaceutical and medical industry.
- Installation in the smallest of spaces
- ATEX-compliant components for the safe operation of sensitive areas
These units are responsible for closing valves during explosions and protecting adjacent equipment. They are flexible for building complex controls in tight spaces. The valve technology approved for ATEX applications is equipped with specially protected coils and cable glands to secure the housing.
PRODUCTS USED
 Are you looking for pneumatic products?
Are you looking for pneumatic products?
Browse through our pneumatic-themed shop
with Metal-Work products.
COMPRESSED AIR TECHNOLOGY IN MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
Here are some of the most important applications of pneumatics in mechanical engineering:
1. MOTION CONTROL:
Pneumatic systems are often used to generate linear and rotational movements in machines. These range from simple lifting and clamping devices to complex robotic arms. Pneumatic cylinders, powered by compressed air, can achieve precise movements and positions.
2. AUTOMATION:
Pneumatic systems are used in automation lines and manufacturing processes to automate tasks such as gripping, sorting, assembling, and packaging products. This increases production speed and efficiency.
3. ENERGY EFFICIENCY:
Pneumatic systems are often simpler and more cost-effective than electrical or hydraulic systems. They are particularly suitable for areas where high speeds and low loads are required. Pneumatic systems can also be energy-efficient as compressed air is quickly released when not in use.
4. SAFETY:
In many cases, pneumatic systems are safer than electrical or hydraulic systems, as compressed air poses a lower risk of malfunctions and personal injury compared to electricity.
5. POTENTIALLY EXPLOSIVE ENVIRONMENTS:
In areas where electrical sparks could pose a danger, such as in explosive environments, pneumatic systems are preferred because they pose less risk.
6. LIGHTWEIGHT CONSTRUCTION:
Pneumatic components are often lighter than hydraulic or electrical systems, making them valuable in applications with limited space or in mobile machinery.
7. CONTROL AND REGULATION:
Pneumatic systems enable precise control and regulation, which is essential in many industrial applications. By varying the pressure and airflow, speeds, positions, and forces can be precisely controlled.
Overall, pneumatics in mechanical engineering offer an efficient, reliable, and versatile way to realize mechanical movements and automation processes.




Are you interested in a solution for your company?

GET IN TOUCH
Technical services
engineering(at)riegler.de
Phone: 07125 9497-642










